How to add a new domain¶
One of the main aims of PyDial is to provide a common statistical dialogue system framework where people are able to create and evaluate dialogues about their own domain. Therefore, adding a new domain has been made very easy. All you need is the respective data base, e.g., about restaurants in Cambridge.
If your data is quite simple (like, eg. CamRestaurants) you might be able to use the ontology creation script explaine din the following section. If you have a more complex domain with custom queries, custom user gal selection, or custom simulator environment, you can learn to load your own implementations in the final section of this part of the tutorials.
Creating a new domain using ontologyTool.py¶
The data base should contain one table containing all necessary information and meet the following requirements:
- The table name should be the same as of the identifyer of the resulting domain.
- All binary slots (which can only hold yes/no values) should be represented as 0 for false and 1 for true.
- The data base should be an SQLite data base.
To create a new domain, all you need to do is to execute the following python tool:
python scripts/ontologyTool.py -n -d NEW_DOMAIN_NAME -db PATH_TO_DB_FILE --type ENTITY_TYPE
The type is the type of the entity contained in your data base. It may be used to distinguish between different domains. As an example, the call to the python script to create CamRestaurants would look like this:
python scripts/ontologyTool.py -n -d CamRestaurants -db ontology/ontologies/CamRestaurants-dbase.db --type restaurant
Doing this will lead you though a step-wise process where you have to select which columns of your data base table are part of which functional set of slots of the dialogue (informable, system requestable, requestable, binary).
First, the script asks for the informable slots. By pressing the number of a slot and confirming it with ENTER, the respective slot gets marked with a star. Once all slots have been chosen, simply press ENTER without a number and you can continue to selecting the next type of slots.
A screen shot showing the selection of all informable slots of CamRestaurants is shown in the following:
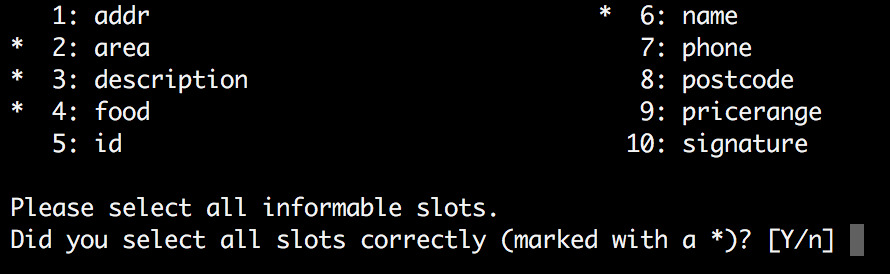
The slot types explained:
- informable: information the user can inform the system about, e.g., food or name
- system requestable: information the system can actively ask the user about to elicit the user's goal, e.g., food but not name
- requestable: information the user can request from the system
- binary: information which is in the form of a yes/no or true/false
Making more extensive changes¶
In this section, we describe how to customize domain behaviour and what to do if your database is not organised in one single table.
Complex table structures¶
If you are able to create ontology rules in a flat format (like ontology/ontologies/CamRestaurants-rules.json) for your domain, you can still use pydial without major changes even if you r table structure is more complex. The Python module which handles each domain may be dynamically loaded using the config file. The respective config entries are in a new section called [ontology_<domainname>], e.g.:
[ontology_CamRestaurants]
handler=ontology.FlatOntologyManager.FlatDomainOntology
The module referenced above also provides the interface description to be used. Please refer to the tutorial "How to add your own module" for a general description on how to add new modules.
Custom simulator behaviour¶
If you need custom user simulator behaviour, you can dynamically load own module implementations as well for the goal generator (which generates the user goals) and the user simulator model which is the core module describing the simulator behaviour. For the latter, there is currently only an implementation available using probabilistic rules but by loading a dyniamic module, this can easily be changed. The config settings are
[usermodel_CamRestaurants]
goalgenerator = usersimulator.UserModel.GoalGenerator
usersimulator = usersimulator.UMHdcSim.UMHdcSim
For the interface definition of the goal generator, the above stated class is used. For the user simulator, all classes inherit from usersimulator.UMSimulator.UMSimulator.